30 Percent Off 40 Dollars
scising
Sep 20, 2025 · 4 min read
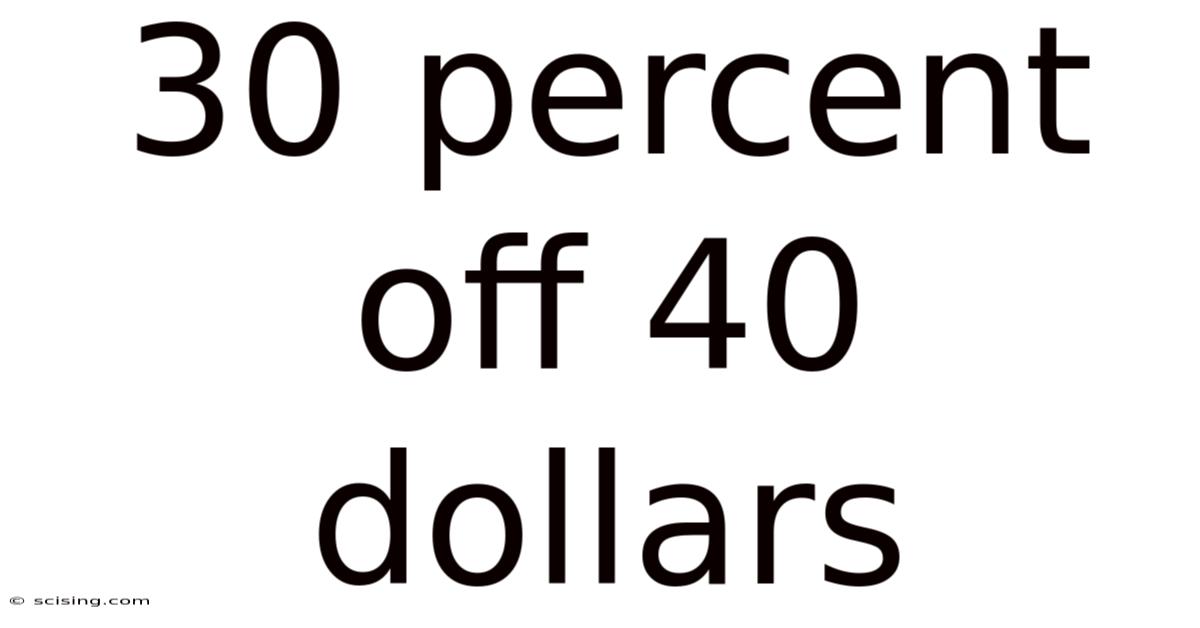
Table of Contents
Decoding the Discount: A Comprehensive Guide to Calculating 30% Off $40
Calculating discounts can seem daunting, especially when faced with percentages. But understanding how to determine the final price after a discount, like figuring out what 30% off $40 is, is a valuable life skill applicable to shopping, budgeting, and even professional contexts. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to calculate this specific discount but will also equip you with the knowledge to tackle any percentage discount problem with confidence.
Understanding Percentages and Discounts
Before diving into the calculation, let's clarify some fundamental concepts. A percentage is a fraction of 100. For instance, 30% means 30 out of 100, or 30/100, which simplifies to 3/10. A discount is a reduction in the original price of a good or service. In our case, the original price is $40, and the discount is 30%.
Method 1: Calculating the Discount Amount Directly
The most straightforward method to calculate the discount is to first determine the actual dollar amount of the reduction. We do this by multiplying the original price by the discount percentage.
-
Convert the percentage to a decimal: To do this, divide the percentage by 100. So, 30% becomes 30/100 = 0.3.
-
Multiply the original price by the decimal: Multiply $40 by 0.3: $40 * 0.3 = $12. This is the amount of the discount.
-
Subtract the discount from the original price: Subtract the discount amount ($12) from the original price ($40): $40 - $12 = $28.
Therefore, the final price after a 30% discount on $40 is $\boxed{$28}$.
Method 2: Calculating the Final Price Directly
This method is slightly more efficient. Instead of calculating the discount amount separately, we calculate the final price directly by using the percentage remaining after the discount is applied.
-
Determine the remaining percentage: If you have a 30% discount, that means you're paying 100% - 30% = 70% of the original price.
-
Convert the remaining percentage to a decimal: 70% becomes 70/100 = 0.7.
-
Multiply the original price by the decimal: Multiply the original price ($40) by the decimal (0.7): $40 * 0.7 = $28.
This directly gives you the final price of $\boxed{$28}$.
Method 3: Using Fractions
For those who prefer fractions, we can also solve this using the fractional equivalent of the percentage. As mentioned earlier, 30% is equivalent to 3/10.
-
Multiply the original price by the fraction: Multiply $40 by 3/10: $40 * (3/10) = $12 (this is the discount amount).
-
Subtract the discount from the original price: Subtract the discount amount ($12) from the original price ($40): $40 - $12 = $28.
Alternatively, since we're paying 70%, which is equivalent to 7/10, we can calculate the final price directly:
- Multiply the original price by the fraction: $40 * (7/10) = $28.
This again yields the final price of $\boxed{$28}$.
Practical Applications and Extensions
Understanding these calculation methods extends beyond simple shopping scenarios. Consider these applications:
-
Sales Tax: After calculating the discounted price, you may need to add sales tax. For example, if the sales tax is 6%, you would multiply the final price ($28) by 0.06 ($28 * 0.06 = $1.68) and add it to the discounted price ($28 + $1.68 = $29.68).
-
Multiple Discounts: Sometimes, you encounter multiple discounts. For instance, a "30% off, then an additional 10% off" scenario. You must apply the discounts sequentially. First, calculate the 30% discount, and then apply the 10% discount to the new price. This is not the same as a 40% discount.
-
Investment Returns: Percentage calculations are crucial in finance. Understanding how to calculate percentage increases or decreases in investments helps track performance and make informed decisions.
-
Budgeting: Tracking expenses and calculating percentages helps in budgeting. For example, determining what percentage of your income is allocated to housing or entertainment.
-
Data Analysis: In various professions, analyzing data often involves calculating percentages and making comparisons.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What if the discount is not a whole number percentage (e.g., 27.5%)?
- A: Follow the same steps, but use the decimal equivalent of the percentage (27.5% = 0.275).
-
Q: How can I quickly estimate a discount without a calculator?
- A: For rough estimations, you can round the percentage. For example, 30% is close to 1/3. You could mentally calculate 1/3 of $40, which is approximately $13. Subtracting this from $40 gives you an approximate final price of $27.
-
Q: What if the discount is applied to a price that includes tax?
- A: The discount should be applied before the tax is added. Otherwise, you are not getting the full discount value.
Conclusion
Calculating a 30% discount on $40, resulting in a final price of $28, is a straightforward process once you understand the underlying principles of percentages. The methods outlined above—direct calculation of the discount, direct calculation of the final price, and the use of fractions—provide versatile approaches to solve this and similar problems. Mastering these methods not only improves your shopping savvy but also enhances your numerical literacy across various aspects of life. Remember that the key lies in understanding the relationship between percentages, decimals, and fractions and applying these concepts systematically. With practice, you'll become proficient in calculating discounts and making informed decisions in all situations involving percentages.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Post Means Before Or After
Sep 20, 2025
-
Fertile Areas In A Desert
Sep 20, 2025
-
Books Written By Amelia Earhart
Sep 20, 2025
-
Bulletin Board Ideas For Classroom
Sep 20, 2025
-
How Far Is An 8k
Sep 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 30 Percent Off 40 Dollars . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.